Caffeine/Energy Drinks
Caffeine/Energy Drinks
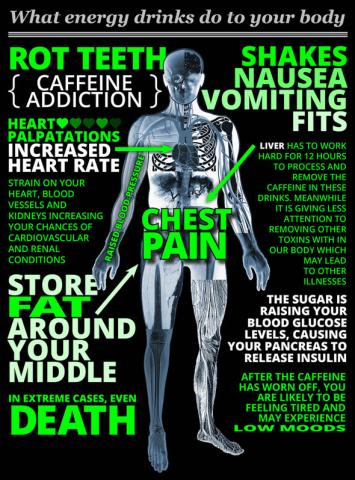
Being in university means many sleepless nights studying or hanging out with friends. Energy drinks are prevalant on campus because these drinks claim to improve energy, help with weight loss, increase endurance, and improve concentration. The main ingredient in energy drinks is caffeine. They also may contain extract from the guarana plant (which is similar to caffeine), the amino acid taurine, carbohydrate in the form of sugar, and vitamins.
Health Concerns About Energy Drinks
- Too much caffeine. A single serving can (most cans are 2 servings) have as much as 180 mg of caffeine, 360mg total. In comparison, there is about 95 mg of caffeine in 240 mL (8 fl oz) of brewed coffee. The maximum daily intake for healthy adults is 400 mg/day and too much caffeine can cause nervousness, feeling grumpy, upset stomach, diarrhea, and headaches.
- Other ingredients. Energy drinks may contain other ingredients, such as kola nut or guarana. There has been little research on how these ingredients may affect the body.
- Sugar. Energy drinks usually contain sugars, which add to the calories. This could lead to weight gain. The sugars can also lead to dental problems.
- Withdrawal. When your body gets used to a lot of caffeine and then you stop using it, you can get symptoms including headaches, feeling tired, having trouble concentrating, and feeling grumpy.
- Sleep. The caffeine in energy drinks may make it harder to sleep. Some people may feel they need less sleep, due to the stimulation they get from the caffeine. This can lead to sleep deprivation.
- Negative effects from mixing with alcohol.
(Source: Myhealth.alberta.ca)
Image